Services
Pancreatic Biopsy
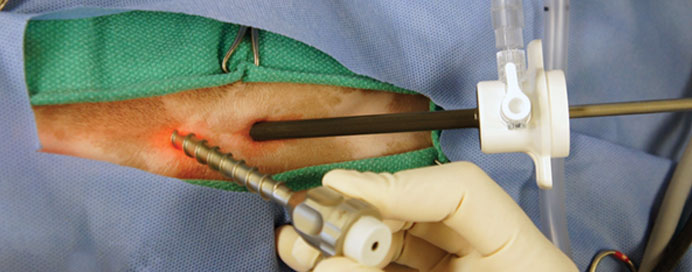
A pancreatic biopsy is a diagnostic procedure conducted to obtain a tissue sample from the pancreas for further examination. This sample helps in diagnosing various pancreatic conditions, including pancreatic cancer, chronic pancreatitis, or autoimmune diseases affecting the pancreas. The biopsy can be performed through different methods, such as fine needle aspiration (FNA) guided by imaging modalities like ultrasound or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), or through surgical biopsy during a laparoscopic or open procedure. During FNA, a thin needle is inserted into the pancreas to collect cells or tissue fragments, while surgical biopsy involves the removal of a larger tissue sample. Once obtained, the biopsy sample is analyzed by pathologists to identify any abnormal cellular changes, tumors, or inflammatory processes. Results from the pancreatic biopsy play a critical role in determining the appropriate treatment plan and prognosis for the patient. While generally safe, pancreatic biopsies carry a small risk of complications, such as bleeding or infection, which are typically minimal when performed by experienced healthcare professionals. Overall, pancreatic biopsy is a valuable tool in diagnosing pancreatic diseases and guiding optimal patient management.