Services
- Hepatology
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatitis
- Liver Transplant
- HCC
Liver Transplant
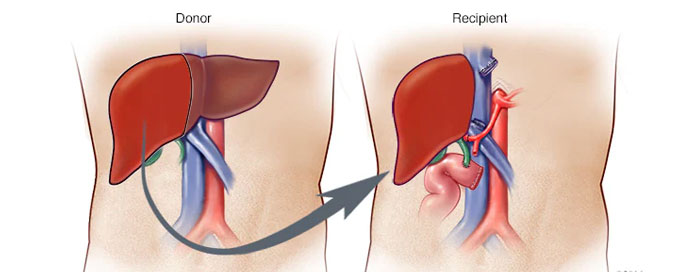
Liver transplant, also known as hepatic transplantation, is a surgical procedure performed to replace a diseased or malfunctioning liver with a healthy liver from a deceased or living donor. It is typically reserved for patients with end-stage liver disease, acute liver failure, or certain liver cancers that cannot be treated effectively through other means. Liver transplantation is considered a life-saving treatment option for individuals with advanced liver disease who have exhausted all other treatment options. The procedure involves removing the diseased liver and replacing it with a donor liver, which is carefully matched to the recipient based on factors such as blood type, tissue compatibility, and medical urgency. Liver transplantation can be performed using either a whole liver from a deceased donor or a segment of liver from a living donor. The success of liver transplantation depends on various factors, including the quality of the donor organ, the recipient's overall health, and adherence to post-transplant medication and follow-up care. While liver transplantation offers the potential for a significantly improved quality of life and long-term survival for patients with end-stage liver disease, it is also associated with risks and complications, including rejection of the donor liver, infection, and side effects from immunosuppressive medications. Close monitoring and lifelong medical management are necessary to optimize outcomes and prevent complications following liver transplantation. Overall, liver transplantation represents a vital therapeutic option for individuals with severe liver disease, providing them with a chance for a new lease on life.